I heard about a volleyball research paper while listening to an episode of the Perception & Action podcast. That paper is How functional movement variability facilitates successful skill adaptation during the volleyball attack by, I believe, a group of Portuguese researchers.
While I think the podcast does a decent job of presenting the ultimate conclusions of the paper, I found it difficult to ascertain from it how the experiment was actually done. Fortunately, that’s pretty clearly outlined in the paper. As the title indicates, it’s about attacking. Specifically, attacking against a block under three conditions:
- Double block taking cross
- Double block taking line
- Split double block allowing an attack at 6
Hitters took turns attacking as part of a serve-pass-set-attack sequence, with three receivers. The attackers were not included among the passers. They each did an equal number of attacks against all three of the above blocking set-ups. There’s a diagram in the paper showing the drill structure.
There were two training groups:
Traditional Approach (TA) group: Each blocking set-up was trained separately. The hitters first faced the block taking cross for 6 balls, then taking line for 6 balls, and finally the split block in the last 6 balls. Or some other variation of the sequence. In other words, the hitters knew what block set-up they were going to face before each rep.
Constraints Led Approach (CLA) group: Here the attackers still spread their attacks evenly across the three block set-ups. The difference here, though, is those set-ups were random. So the hitters didn’t know before each rep which kind of block they faced.
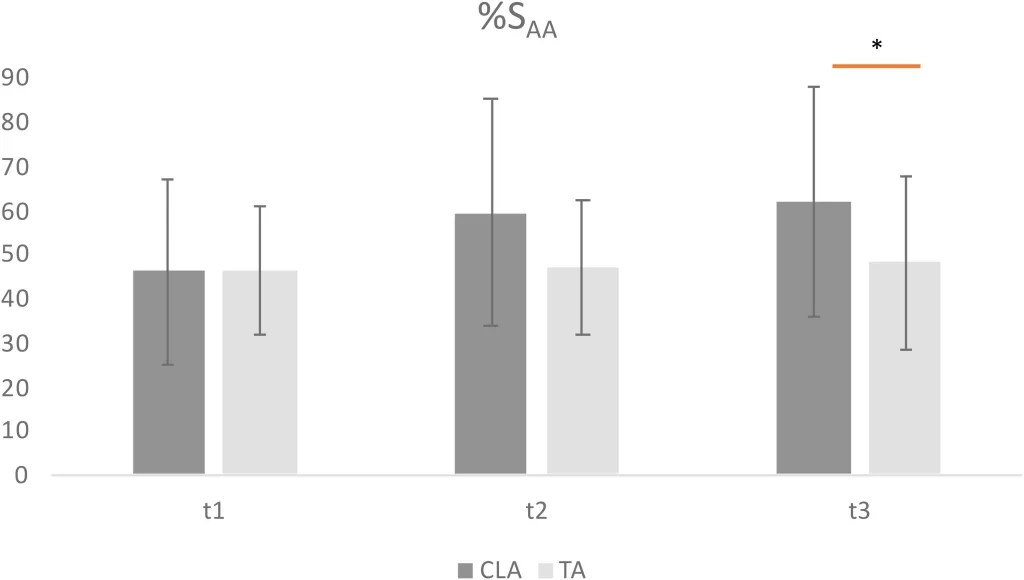
There’s a whole section on spacial temporal variables. You may find that interesting, though it’s pretty technical. For most of us, the key bit is the attack performance the results from the preliminary test (t1), immediately following 6 weeks of training (t2), then finally somewhat later to test retention (t3).
Here’s the graph showing the results for the two groups:
As expected, the two groups showed the same performance before the training. While the TA group showed little gain from the training, the CLA group improved markedly, and even extended the gain slightly in the retention test. The * in the graph indicates a statistically significant difference.
Makes sense when you think about it, right? Real attacking situations involve uncertainty about what the hitter will…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Coaching Volleyball…